Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

When it comes to building strong, well-developed shoulder, several exercises correspond to the efficiency of the above-ground press and press the press. Although they can look similar at first glance – they both move on the tile from the shoulders to the above-ground – their stimulus training is extremely different. Error prints emphasizes muscle control and hypertrophyWhile thick pressing affects Explosive power and a total body.
This article is in a detailed comparison of presses and push press, examining their mechanics, muscle activation forms and finally, which exercise rules the tops for maximizing hypertrophy and strength.
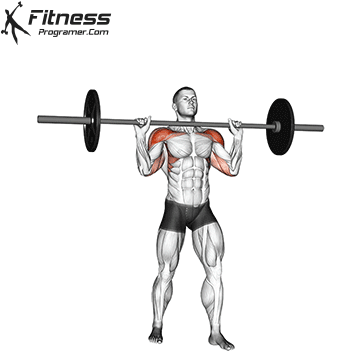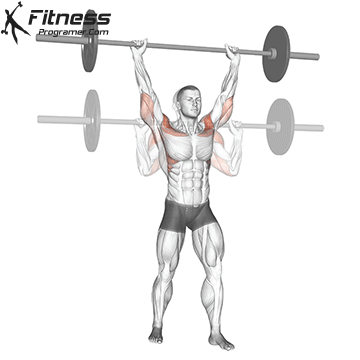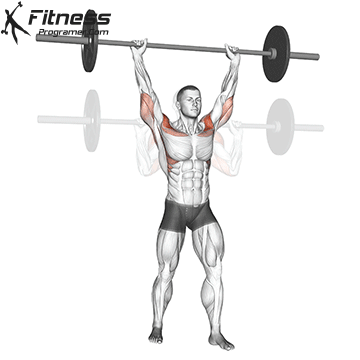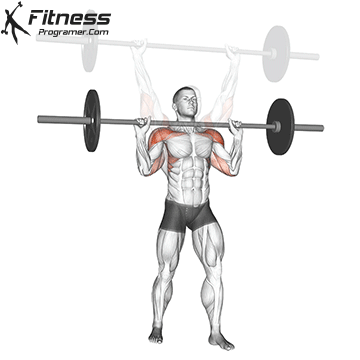
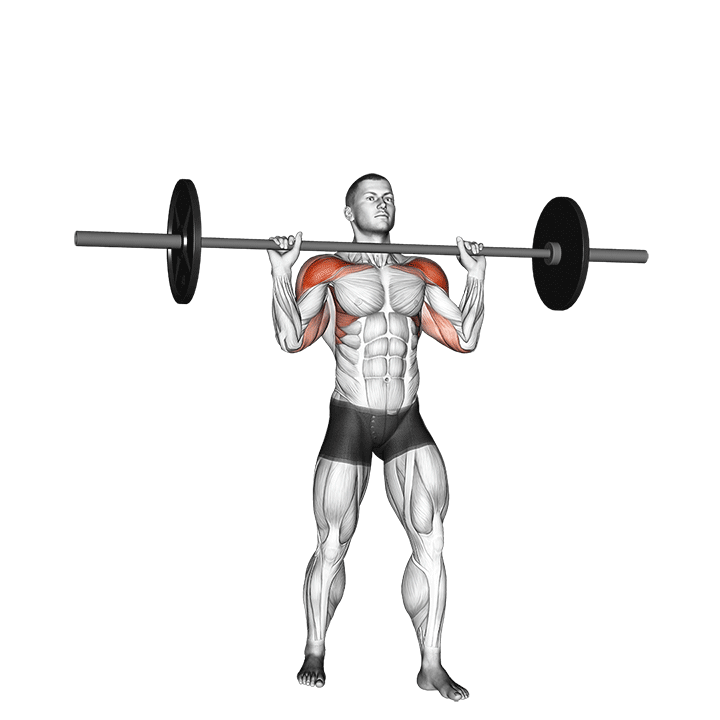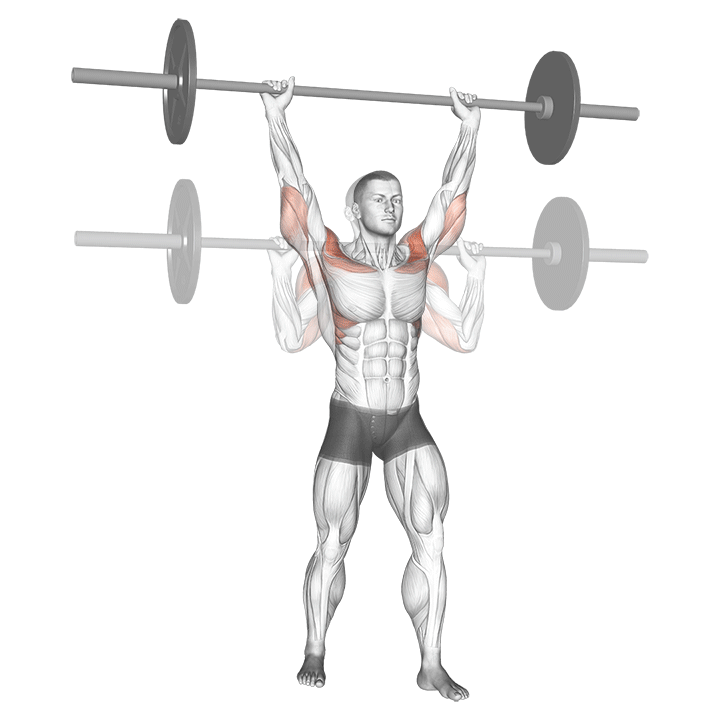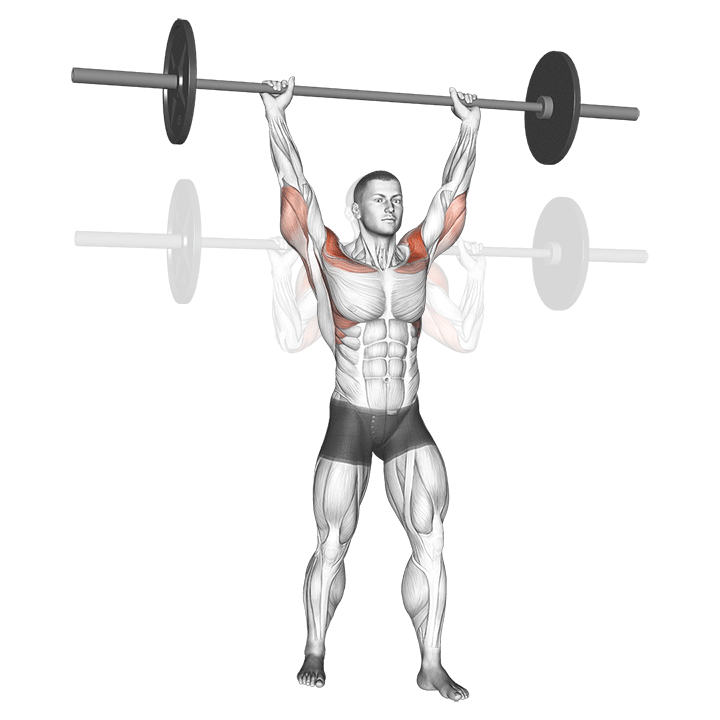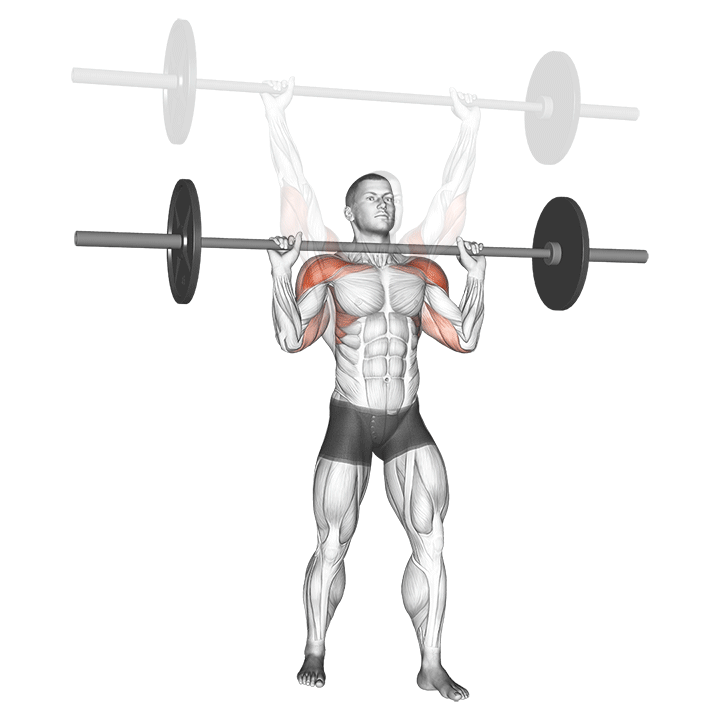
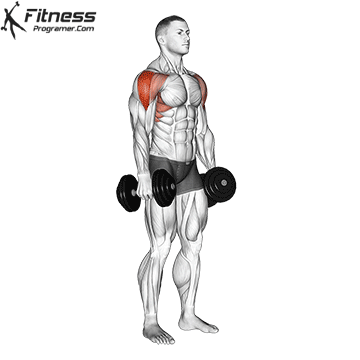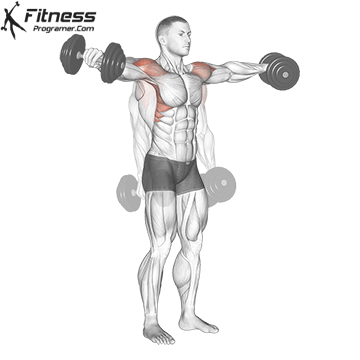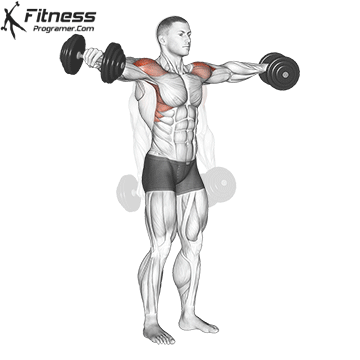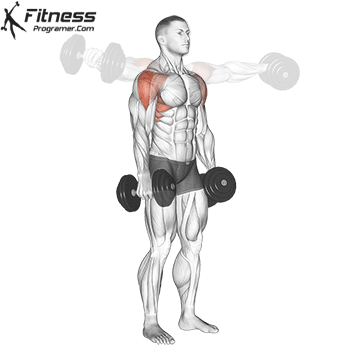
The overheadcommonly called military pressIncludes pressure on barbames from shoulders directly over the head There is no swing from your feet. All movements generate upper body, and the lift is usually performed in a standing position, requires rigid basic engagement and Scapular control.
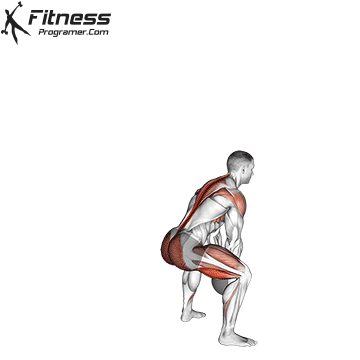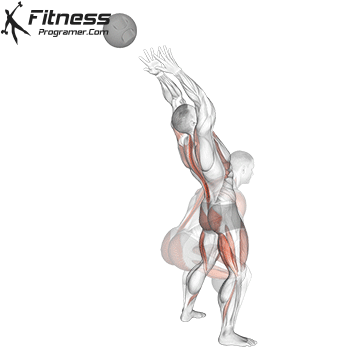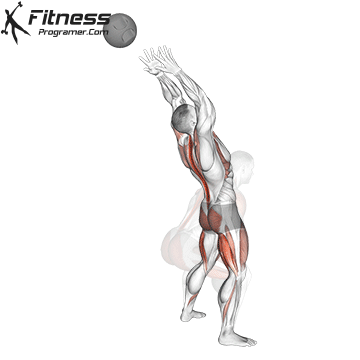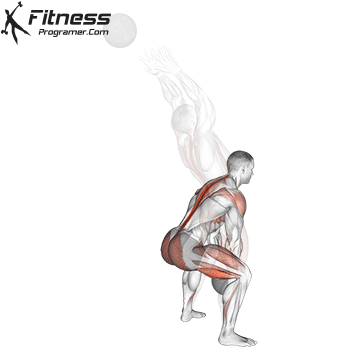
The pressing It is a dynamic overhead motion that begins with a shallow diploma and hip and knee drive, transmission from lower body in Barbal to help pressing pressing. Although it allows the harder loads to be abolished reduces muscle insulation shoulder.
| Training variable | Overhead | Pressing |
|---|---|---|
| Tension time | High | Moderate to low (due to speed) |
| Shoulder insulation | High | Moderately (shared with a leg ride) |
| Cargo potential | Moderate | High |
| Explosiveness | Low | High |
| Repetition control | High (slower tempo) | Moderately (Momentum-aiding) |
| The best for | Hypertrophy, control, stability in common | Power, overload, athletic transmission |
Though Push Press allows greater external loadsThese loads partially absorb Kinetic chain-Specific during starting movement resulting Less deltoid activations per tail compared to overhead pressure.
For muscle growthThe overhead is superior due to a long time under tension and deltoid increased load throughout the range of movement. Push Press, while allowing harder weight, it is a bit removed below the lower part and shortens the period of active shoulder tension.
That was said, the Push Press is not useless for hypertrophy-Speciated when used as Extra lift After an overhead pressure for overloading the neuromuscular system or when introducing variety for experienced cranes.
When the goal is Maximizing overhead power and explosive shoulder powerThe pressing It clearly exceeds overhead pressure. Leg drive allows athletes to raise more weight at speed, making it ideal for sports performance and Olympic preparations for lifting.
Push Press improves coordination via kinetic chain and boosts The force of force developmentwhich is crucial in explosive athletic movements such as throwing, throwing and jumps.
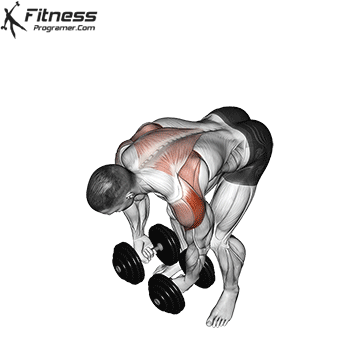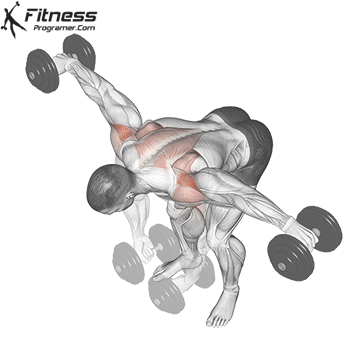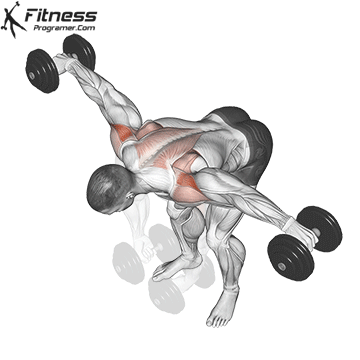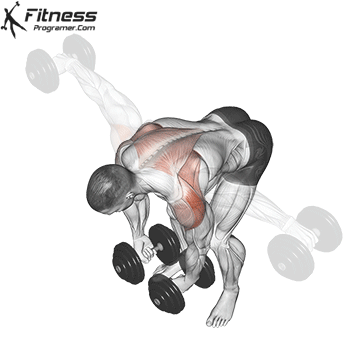
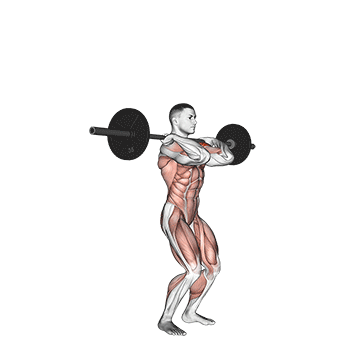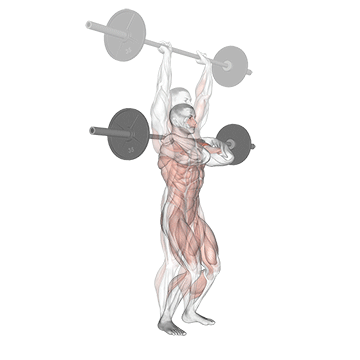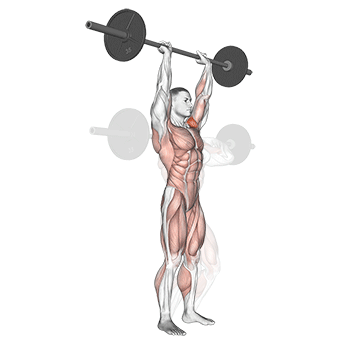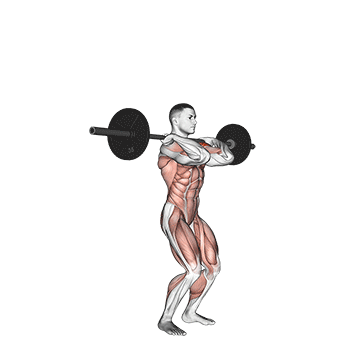
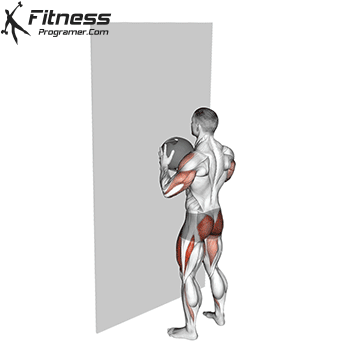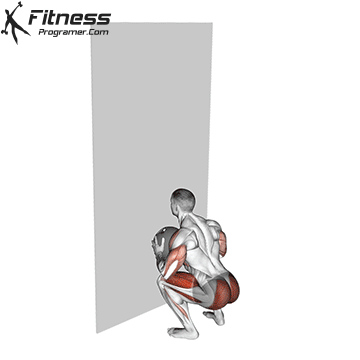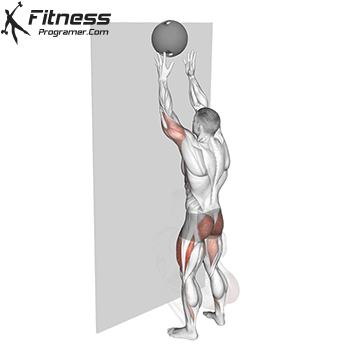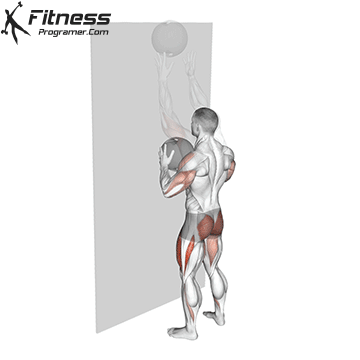
The overhead and pressing Serve different but complementary roles in strength training program. For those seeking The greater size and shoulder formThe overhead is more efficient means due to mechanical insulation and incentive of focused hypertrophy. In contrast, the pressing It is ideal for development Explosive shoulder strength and full body body strengthespecially in athletes and advanced lifters.
Strategic combination of both elevators – depending on your training and goals phase – can give impressive winnings in and muscle mass and performance.