Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Entering the gym is one of the best things you can do for your body, but without real approach, it can also lead to strains, an ingrain injury. Conzistential discs results in strength training, hypertrophy or general fitness. The injury not only submits you per week – can undo the months of progress, create chronic pain and disrupt motivation. Prevention of injury is not only about avoiding accidents – it is about creating conditions for long-term progress, consistency and performance.
Studies show that most injuries in the gym occur from poor techniques, inappropriate load management and ignoring routines of heating or recovery (ACSM, 2021). Therefore, the prevention of injury should not be long-term programming, but an important part of it.
Learn to prevent injury from the gym with our expert allows. This guide teaches you how to warm, use the appropriate shape and stay safe during your exercises.
Jumping right into heavy lifting or intense cardio without the preparation of your body is one of the fastest ways to hurt. Warming Prepares a neuromuscular hard work system. Cold, stiff muscles are less elastic, increasing the risk of muscle stress or spraying ligaments. Heating is also the main central nervous system, making movements faster and coordinated.
Proper heating:
Recommended Protocol:
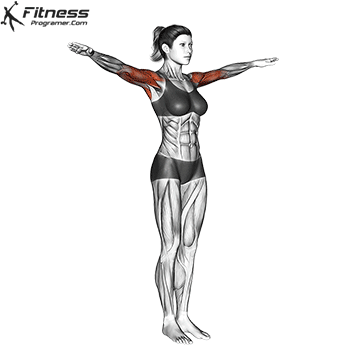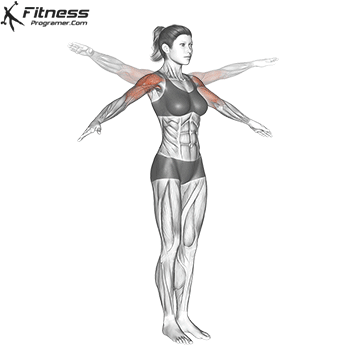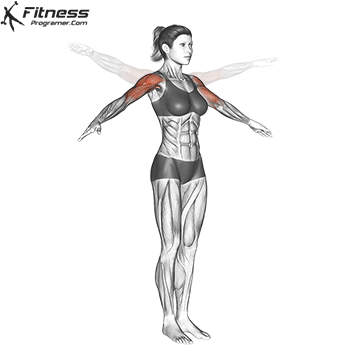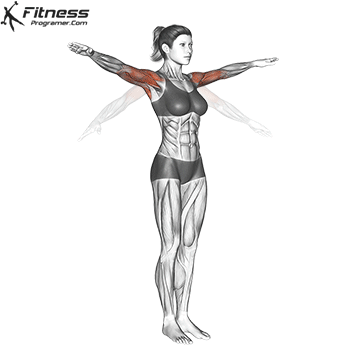

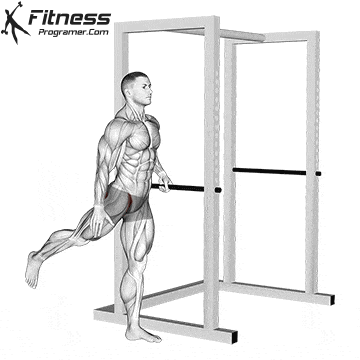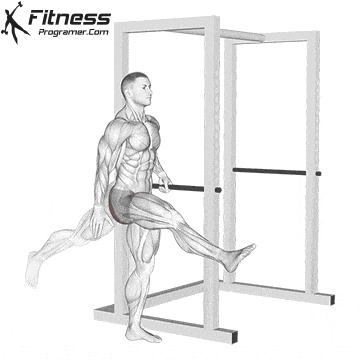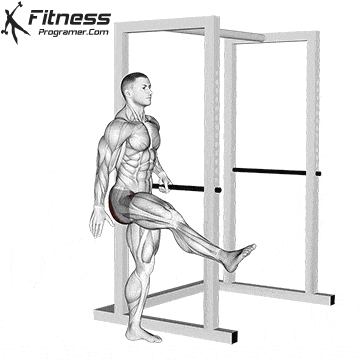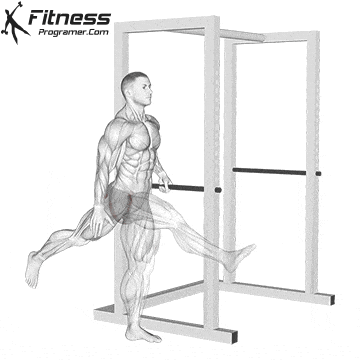
Science Note: Behm & Chaouachi (2011) showed that dynamic heating improves sprint, jump and lifting performance, while reducing the acute risk of injury.
The bad form is the leading cause of the gym injury. Focus on learning the correct mechanics of movement before increasing intensity. Even small deviations in the form can overload joints or soft tissue. For example:
How to improve the technique:
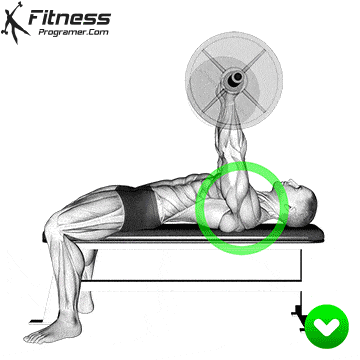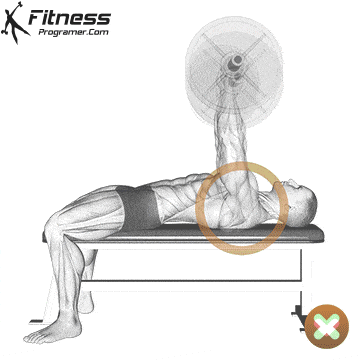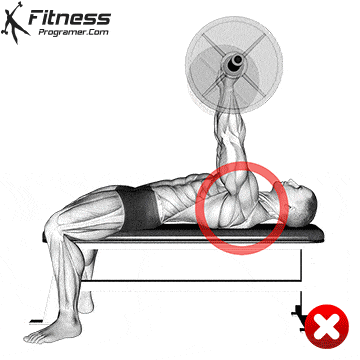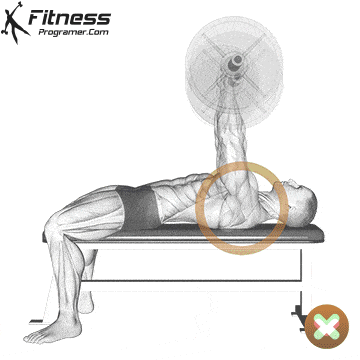
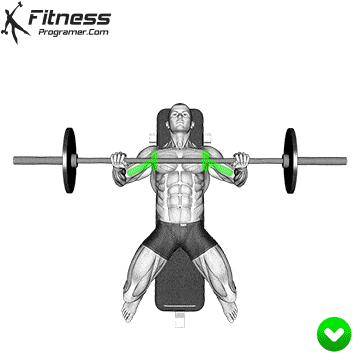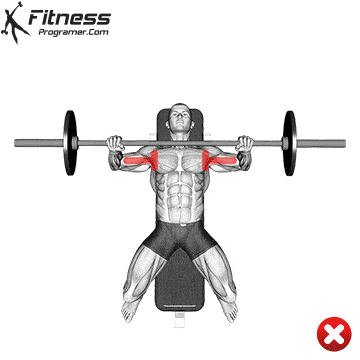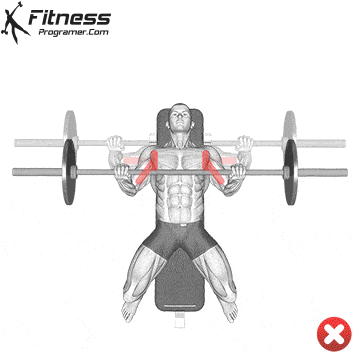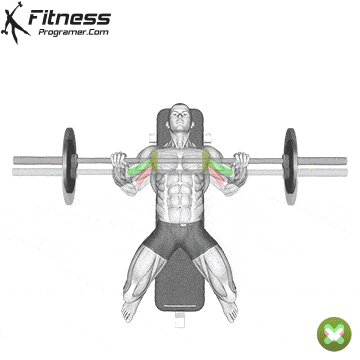
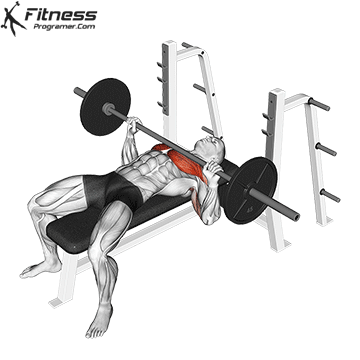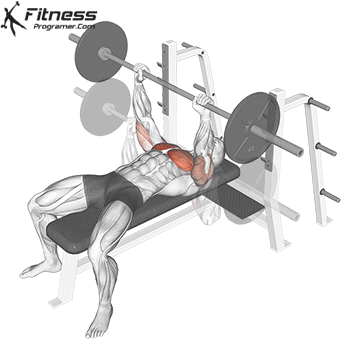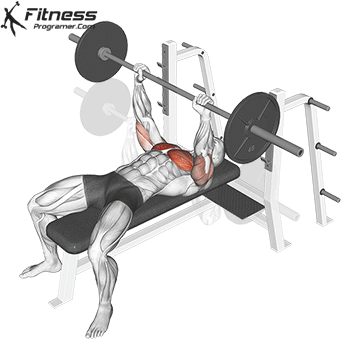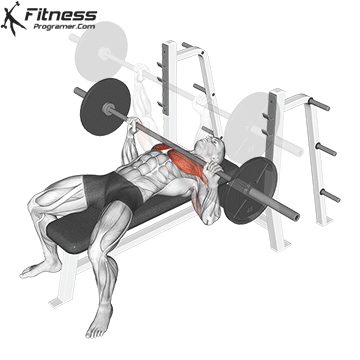
The body is best adapted when the workouts are increased in small, manageable steps. Drastic jumps in weight or volume can be emphasized joints, tendons and muscles. Muscles, tendons and ligaments are adapted to different prices. While the muscle power increases the relatively fast, connective tissue lasts longer to rearrange, making a sudden load jumps the usual cause of injuries.
Safe Guideline for Progress:
Example: If you are a bench press 60 kg for 3 × 8, do not jump to 80 kg. Go to 62.5-65 kg or add a tail / additional set before increasing load.
The muscles are growing and adjusted during the holiday, not only during exercise. Neglects recovery often leads to injuries affected tired.
Key recovery strategies:
Powerful premiere (four-legged, pecs, lattoes) often share less stabilizing muscles, leaving exposed joints. Weak stabilizers – such as the cuff rotator in the shoulder or hook abstract – can jeopardize the quality of movement. Incorporate work work to reduce the risk of injury:
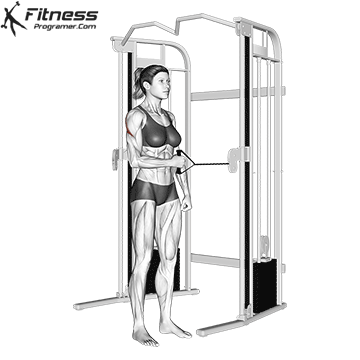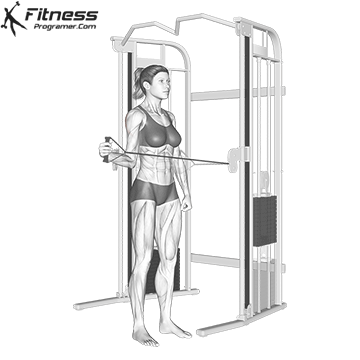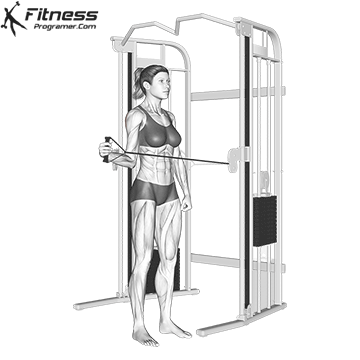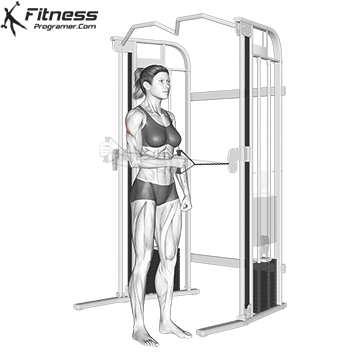
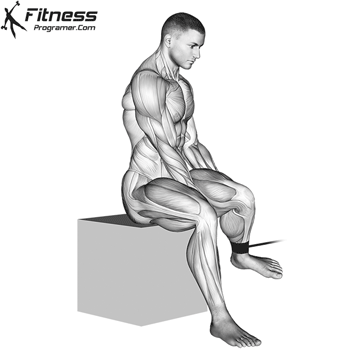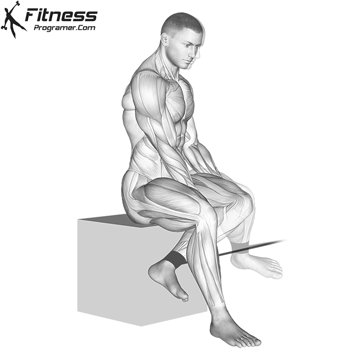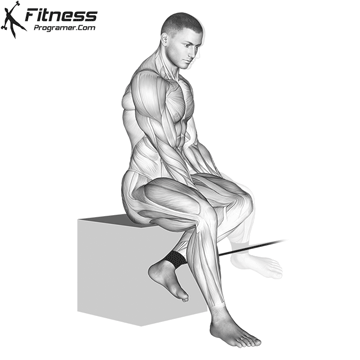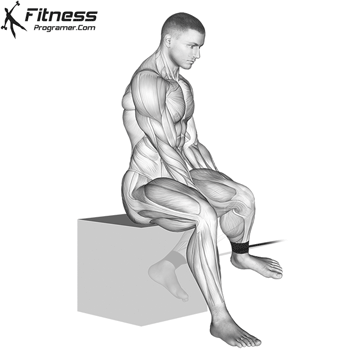
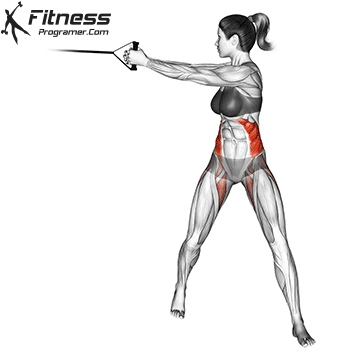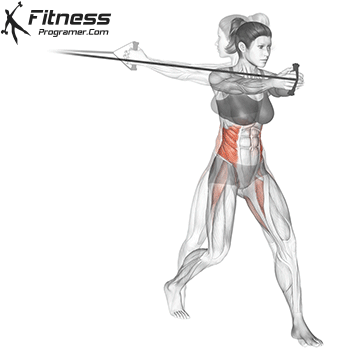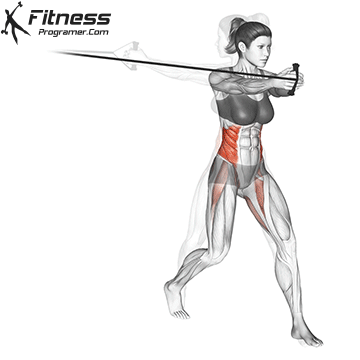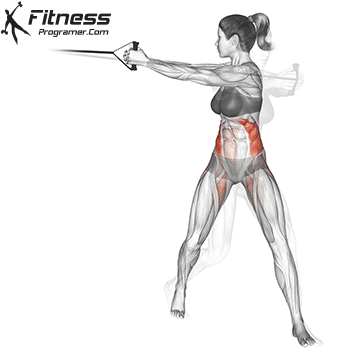
Research: Weak hip abductors are associated with ACL and patellofemoral injuries in athletes (Hevett et al., 2005).
Sharp pain, discomfort of shared or long-lasting sickness are signals, not obstacles to go through. Training should feel challenging, but never painful.
Ignoring It is a path to overuse injuries like tendinitis or stress fracture. Set the exercise selection, reduce the load or contact physiotherapist.
Avoiding a gym injury is not to be careful for stagnation – it’s about smarter for training. By combining solid techniques, gradual advancement and adequate recovery not only to protect your body but also create a long-term strength and muscle growth.
References